Reduction and Reuse
General Information
Strategies and interventions aimed at reducing the use and promoting the reuse of plastic products. This approach involves eliminating unnecessary and/or avoidable packaging, minimizing packaging where possible, and encouraging consumer behaviour that prioritizes reuse. Reduction and reuse are critical interventions because studies have shown that without these upstream interventions, it will not be possible to meaningfully address plastic pollution given that waste management infrastructure alone cannot cope with the exponential growth of plastic waste.
There are two main types of reuse models: Business-to-Consumer (B2C) and Business-to-Business (B2B). Within B2C there are four distinctive subtypes of models as described by the Ellen MacArthur Foundation, depending on whether the consumer refills the packaging themselves or returns it to the business, and whether that refill/return takes place at home or on the go.
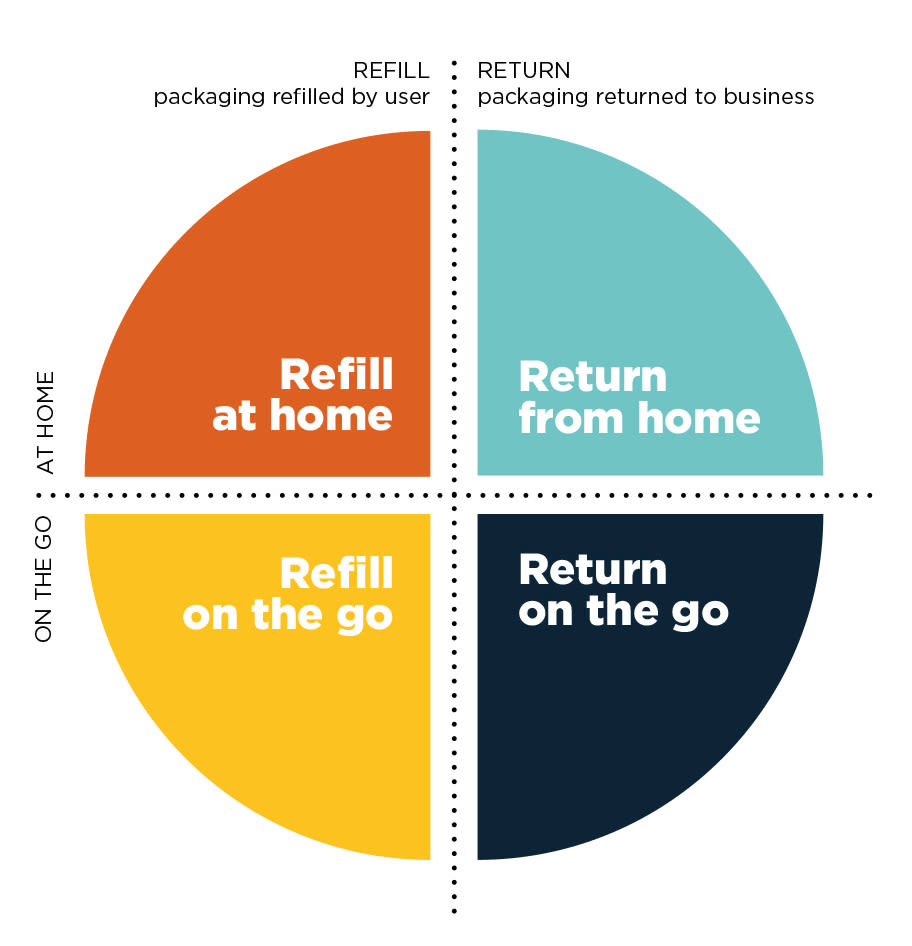
Source: Ellen MacArthur Foundation, Reuse – rethinking packaging (2019, p.7).
B2B reuse models such as reusable pallets, crates, foldable boxes, pails, drums, and various alternatives to flexible pallet wraps have seen greater adoption compared to their B2C counterparts. Large scale reuse systems come with benefits including shared costs and lower resource consumption. B2B operations have also seen the emergence of 'reuse-as-a-service' providers, and the market is predicted to continue its growth trajectory.
Reduction and reuse potential is particularly high for bottle packaging, transport packaging (B2C and B2B film), and refill applications.
Optimised reuse cycles and logistics can lead to a 13% reduction in packaging demand by 2030 and 30% decrease in plastic packaging and the resulting waste by 2050, while cutting GHG emissions by 26% (Systemiq (2022). ReShaping Plastics: Pathways to a Circular, Climate Neutral Plastics System in Europe ).
At scale, these models have multiple benefits:
-
Potential cost reductions: At scale, well-designed and successful reuse models may offer significant cost savings and drive efficiency in the supply chain. Passing cost savings on to consumers will help incentivize customers to adopt reuse, while maintaining profit margins for retailers/brands. Algramõ reports that its platform refill system, for example, not only allows firms to save 30% of costs but also offers refill products at low prices. Concentrated refill capsules, such as Everdrop's cleaning tablets, on the other hand, can save up to 80% of transport costs by avoiding the need to transport water (Ellen MacArthur Foundation, Upstream Innovation: A guide to packaging solutions, p.82). Companies are encouraged to complete a cost analysis of a reuse model for their packaging format.
-
Personalized user experience: Carefully designed reuse models can bring consumer benefits, including improved choice, more automated deliveries, and the ability for customers to mix and match flavors, personalize packaging, and choose desired quantities (Ellen MacArthur Foundation, Rethinking Packaging ). PepsiCo's SodaStream, for example, reduces space and travel requirements, as there is no need to carry water bottles, and accommodates user preferences by offering different flavors (Ellen MacArthur Foundation, Upstream Innovation: A guide to packaging solutions, p.84).
-
Stronger customer relationships: Subscription schemes for reusable packaging create long-term customer relationships and boost brand loyalty and customer retention. Bite toothpaste bits, for example, offers auto-refill subscription models, sending refill bites every four months. In addition, by incorporating digital offerings, firms can gather information on user preferences and improve system performance (Ellen MacArthur Foundation, Upstream Innovation: A guide to packaging solutions, p.80).
-
Lower emissions and plastic pollution: When well implemented, reusable packaging may reduce GHG emissions and plastic pollution compared to single-use plastic.
Costs and revenue model
Return business models' Opex and Capex are highly sensitive to economies of scale , system design and efficiency, including level of shared collection, sorting and cleaning infrastructure, packaging standardisation and pooling, return rate and scale.
Costs for B2C return systems are roughly evenly split between production packaging, and return/refill costs (i.e., transportation, collection, sorting, and cleaning). An estimated 80% of total costs are operational expenditures, of which 60% are labour costs. Collection costs represent 35% of the total return costs and include collection, reverse transport logistics, and sorting and cleaning).
Modelling system costs at today's prices, highly scaled returnable packaging systems, built collaboratively from the outset, can compete on cost for beverage (6% per unit of utility cost saving vs. single-use (SU)) and personal care (14% per unit of utility cost saving vs. single-use (SU)) sectors. However, food applications likely require additional enabling conditions (e.g. higher EPR fees, virgin plastic tax, carbon tax) to make the economics work due to lower costs per unit for the single-use equivalent packaging for the reusable packaging to compete with.
B2B models, most common of which is "Reuse as a service", are more established and can be profitable, while the majority of B2C models still lack maturity. “Reuse as a service” refers to the service that a business might handle the reuse system on behalf of a restaurant or café, offering the items required for food delivery (cups, containers, etc.) and then taking care of the washing, collection, and redistribution (e.g. Globelet, Ozzi). Successful business models exists, for example Svenska Returnsystems , a reusable packaging provider for the food and beverage industry, has shown a 25% cost savings for its client companies by switching from single use packaging to reusable crates.
A detailed analysis of costs and GHG impacts of different reuse models for different applications and how to make them work can be found in the Ellen MacArthur Foundation (2023). Unlocking a reuse revolution: scaling returnable packaging report.
Investment Readiness Assessment
The investment readiness assessment uses a scoring system across three key parameters to provide a comprehensive view of the investment viability of the finance demand opportunities. Scores vary from 1 to 5. Investors and stakeholders can use this scoring system to make informed decisions and prioritize investment options based on their specific objectives and risk tolerance.
-
Investment Scale
1Projects are usually small scale, although they need to integrate with existing infrastructure, including collection, sortation, and cleaning facilities. A system-level approach with shared infrastructure allows for a capex-efficient deployment of these solutions.
Examples of large scale projects exist although they are limited to specific geographies with favourable regulations, such as France and Germany in the case of reusable takeaway containers.
Scale can be achieved through syndication of small-scale projects into incubator funds
-
Return Potential
2Outside from select few e-commerce opportunities, most solutions in this sector offer low to medium level return on investment. Studies show reusable food containers system providers can achieve low double-digit ROI (The economics of reuse systems (2023, p.24)). Market momentum for reuse and reduce initiatives can grow on the back of favourable regulatory developments and change in public awareness which are expected in the next few years, especially in the EU.
Favourable regulation as a result of the Global Plastics Treaty could, for example, improve the return potential and reduce the risk for these investments.
-
Perceived Risk
4While some B2B models are proven and tested business models, the majority of consumer solutions are in their early stages and face significant commercial and implementation risks.
Grant funded pilot programs and feasibility studies can significantly improve the ability for commercial investors to assess commercial and implementation risks.
Sources of capital for Reduction and Reuse
Primary sources
Secondary sources
B2B models are attractive to commercial capital providers such as venture capital and private equity firms, especially those who have patient capital and can await for the regulatory changes that are expected to boost reuse solutions. Well established B2B models such as reusable pallets and crates have attracted significant commercial capital. Brambles, one of the largest provider of pallets, crates, and containers is a publicly listed company on the Australian Securities Exchange with annual revenues of over $5 billion. Private sector actors looking to adapt to changing consumer choices while also having a positive societal impact also invest in reduction and reuse models.
While the role of commercial capital is expected to continue growing, philanthropic grants are often needed to support the early development of these business models (especially B2C, which are more vulnerable to market volatility) until they further mature and flourish. Grants from donor agencies and governments and concessional capital are often needed to complement and reduce the risk of new initiatives. Therefore in the near-term and in emerging markets philanthropies and charities, governments, donor agencies and impact-first investors will likely continue to drive capital supply, as entrepreneurs experiment with business models and regulations evolve. In one example, the city of Aarhus, Denmark is rolling out a city-wide pilot to scale standardised, reusable cups in partnership with TOMRA See also Case Studies library. In this case, the municipality has invested the required amount to ensure reusable cups are cost-competitive with the single use alternative. As the program scales, the required investment is expected to be reduced, until it can be eliminated altogether.
EPR funds may be shifted towards reuse solutions. For example, CITEO and Adelphe, the French EPR funds, has allocated financing towards a reuse system incubation initiative called project reUse. If implemented at scale, reuse solutions may benefit from a large boost of investment.
De-risking instruments
Companies with access to public market capital can benefit from the emergence of Sustainability-Linked Bonds whereby the financing structure of the bond is directly linked to reduce / substitute targets. While the bond doesn't directly fund reduce and substitute initiatives, it can lower the overall cost of capital for the companies and allow them more flexibility in their overall sustainability strategy.
Enabling System Conditions
Examples of policy interventions that support Reduction and Reuse
-
EU Single-Use Plastics Directive (2019): This law bans certain single-use plastic items (like cutlery, straws, and polystyrene containers) and requires EU member states to promote reusable alternatives. It also sets targets for reducing plastic consumption and improving waste collection and recycling. It is applicable across 27 EU countries. Specific EU countries have included even more ambitious legislation such as France’s Anti-Waste Law (2020) that gradually phases out disposable plastic packaging, including a ban on plastic packaging for fruits and vegetables and requiring restaurants to use reusable tableware for dine-in customers starting in 2023.
-
California’s SB 54 (2022): Also called the Plastic Pollution Prevention and Packaging Producer Responsibility Act, this law mandates that 100% of packaging in California be recyclable or compostable by 2032, with a strong focus on reusable alternatives and extended producer responsibility (EPR) programs.
-
UK Plastic Packaging Tax (2022): This tax applies to plastic packaging that contains less than 30% recycled content, encouraging companies to shift to more sustainable materials and reusable options.
-
Chile’s Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) Law (2016, updated 2021): This law requires companies to take responsibility for managing plastic packaging waste, encouraging reusable and recyclable alternatives. It also includes a ban on single-use plastics in food establishments, promoting reusable options instead.
-
India’s Single-Use Plastic Ban (2022): India has banned a range of single-use plastic items, such as cutlery, straws, and packaging materials. The government has also promoted reusable alternatives through incentives for startups and businesses developing sustainable packaging solutions.
-
Kenya’s Plastic Ban (2017, expanded 2020): While Kenya’s strict ban initially focused on plastic bags, it was later expanded to include single-use plastics in national parks, beaches, and protected areas. This has driven innovation in reusable packaging solutions, particularly in retail and hospitality.
-
Colombia’s National Plastics Law (2022): This legislation phases out single-use plastics by 2030 and encourages reusable alternatives in foodservice, retail, and manufacturing. It also includes an EPR system to promote circular economy initiatives.
For additional examples and detail, the Reuse Policy Playbook (2022) by Upstream offers a comprehensive guide to implementing policies that promote reusable systems. It features examples of local ordinances that have successfully encouraged reuse, serving as templates for other jurisdictions.
Other enabling conditions
-
Shared infrastructure: Reuse business models can more easily achieve economies of scale and high user adoption through shared infrastructure across the value chain (collection, sorting, cleaning, and transportation). Businesses can leverage combined technical expertise to plan and develop this shared infrastructure, while policymakers can implement financial measures (e.g. EPR, taxes, subsidies) to ensure financial viability and incentive widespread adoption and investment in shared infrastructure.
-
Supply chain and logistics improvements: Reuse and return business models require significant re-organization of logistics, including implementation of collection infrastructure, logistics network, and the creation of sorting and cleaning centres, which is currently a major barrier as reverse logistics are costly.
-
Standardisation and pooling of packaging: Packaging and delivery standardization and pooling are key drivers of reuse and return system's environmental and economic outcomes, unlocking economies of scale and greatly reducing logistic complexity and costs.
Financing challenges
-
Lack of pipeline and unproven business model: B2C reuse solutions are still in their infancy and prone to market volatility. Further investment and scale are needed to support the development of these business models to full maturity.
-
Reliance on progressive policies on circularity and changing demand patterns: Evidence suggests market demand for reuse and substitute solutions is largely driven by regulation targeted at enforcing production choices and/or shifting consumer preferences. The majority of investment capital to date has been deployed in Europe and North America.
-
Restrictive policy: Some policies may restrict reusing and refilling containers for certain applications (e.g. food packaging, cosmetics, healthcare)
-
GPAP Report 2022Read More
Aarhus City Deposit System
Aarhus Municipality and TOMRA enter collaboration to establish a deposit system for takeaway packaging
-
 GPAP Report 2022Read More
GPAP Report 2022Read MoreAlgramo — B2C packaging reduce and reuse model
Chilean start-up Algramo expanding its packaging reuse model abroad
-
 IFC Case StudyRead More
IFC Case StudyRead MoreBelgrade Waste-to-Energy Project
Public-private partnership combining de-risking and private sector innovation to support waste management in Serbia
-
StartupRead More
B'ZEOS Seaweed Packaging
Using science and seaweed to tackle the plastic pollution problem
-
 GPAP Report 2022Read More
GPAP Report 2022Read MoreCoca Cola FEMSA Green Bond
Bottling company catalyzing growth of rPET infrastructure in Mexico
-
Katpult OceanRead More
Fortuna Cools
A Philippines-based agritech startup making sustainable coolers out of coconut fibre, supported by seed funding to ramp up production
-
 GPAP Report 2022Read More
GPAP Report 2022Read MoreIndorama Ventures Blue Loan
The world's first blue loan to expand recycling capacity across emerging markets
-
KfWRead More
Landfill in Albania
Funding from KfW to finance landfills in Albania
-
GPAP Report 2022Read More
Natura Sustainability Linked Bond
Issuing the first Latin American Sustainability-Linked Bond (SLB) to target plastic reduction
-
PabocoRead More
Paboco Joint Venture
Paboco to produce fully recyclable paper bottles in 2024
-
Plastic EnergyRead More
Plastic Energy
Chemical recycling company fuels its growth through institutional fundraising
-
STOPRead More
Project STOP Indonesia
Project STOP collaborates with city governments in Indonesia to establish waste collection and sortation systems, supported by grant funding from corporate partners and donor agencies
-
GPAP Report 2022Read More
Recykal
A digital marketplace for plastic waste transactions in India
-
ODARead More
Solid Waste Management Project in Peru
ODA loan agreement with Peru to develop landfills in Peru
-
GPAP Report 2022Read More
Tridi Oasis
An innovative recycling startup in Indonesia proves resilient with the help of early-stage blended finance
-
JICARead More
Waste-to-Energy and Waste Treatment Project in Vietnam
Chemical recycling company fuels its growth through institutional fundraising
-
Government FundingRead More
Bueno Aires waste collection systems
Providing waste collection services to the municipality of Buenos Aires, Argentina
-
Private EquityRead More
IFCO acquisition by PE fund Triton
Reusable packaging solutions provider acquired by Triton and a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Abu Dhabi Investment Authority (ADIA), for US$ 2.51 billion
-
CircolutionRead More
Circolution receives seed funding from Amcor
Amcor, a global packaging solutions leader, has invested $250,000 into smart reusable food packaging start-up Circolution
-
NotplaRead More
Notpla raises £10M to develop seaweed-based packaging
London-based Notpla, a sustainable packaging startup, announced that it has raised £10M in its Series A round of funding
-
USAID ReportRead More
Indonesia's Waste4Change raises $5m in series A funding
Indonesia-based waste management platform Waste4Change announced Friday that it has secured a $5 million series A funding round
-
COLIBARead More
Coliba Africa
Coliba Africa secured $850,000 from USAID and support from the Alliance to End Plastic Waste to train 6,000 waste collectors and establish recycling facilities with a 14,000-ton capacity.
Aarhus City Deposit System
Aarhus and TOMRA have joined forces to create deposit system for takeaway packaging in the city center of Aarhus. The municipality and the company have signed a collaboration agreement for a three-year trial, which initially focuses on take away cups with a deposit. In next stages the plan is to expand the system to also cover all types of takeaway packaging ensuring a convenient and circular system. The pilot reuse system will enable the shift from single use packaging to reusable packaging, by providing an infrastructure that entire cities can use.
TOMRA and Aarhus City enter collaboration to create innovative reuse system
Algramo — B2C packaging reduce and reuse model
Founded in 2012, Algramo initially pursued a model facilitating reuse of household containers that used tricycles fitted with dispensers to sell non-perishables like rice and laundry detergent to low-income families in Chile. It then established vending machine dispensers — with reusable containers that enable consumers to buy exactly the amount they want — in retail outlets in poorer areas of Santiago. Having raised over $11 million in aggregate over two funding rounds in 2019 and 2021 from US, Mexican, and European investment funds, Algramo is now expanding its reuse model, using radio-frequency identification (RFID) tagged containers in the US, UK, Mexico, and Indonesia.
GPAP (2022), Unlocking the Plastics Circular Economy: Case Studies on Investment
Belgrade Waste-to-Energy Project
In 2015, the City of Belgrade started working with IFC to design a public-private partnership to overhaul the city's waste management system focused on the Vinča landfill. The project, which received €260 million in financing and guarantees from IFC, MIGA, and others, including a €20 million blended concessional loan from the Canada-IFC Blended Climate Finance Program, was managed by a consortium including Veolia, ITOCHU, and Marguerite Fund II. The integrated Vinča project includes a new energy recovery facility, a cogeneration facility, and a construction and demolition waste recycling plant, alongside a new sanitary landfill meeting EU and Serbian standards. Operational since February 2023, the waste-to-energy facility processes up to 340,000 tons of waste annually, generating up to 30 MW of electricity and 56 MW of thermal energy, enough for 30,000 households' electricity and 60,000 households' heating. The recycling plant handles 200,000 tons of construction waste per year. This initiative is expected to cut Belgrade's greenhouse emissions by 210,000 tons of CO2 equivalent annually and has created 120 permanent and 600 construction jobs. This is also notably the first large-scale private sector waste management project in emerging markets and the first in Serbia to receive Gold Standard Carbon Credit Accreditation.
Belgrade’s Waste-to-Energy Project Sparks Environmental Renaissance
B'ZEOS Seaweed Packaging
The Norwegian start-up B'ZEOS develops novel bio-based packaging solutions with the aim to replace the need for single-use plastic. B'ZEOS has received grants from Innovation Norway and the EU via an R&D funding scheme for the blue bioeconomy. The company has collaborated with Nestlé in the development of food packaging prototypes, from edible straw formulation to pilot scale manufacturing of flexible films packaging.
Coca Cola FEMSA Green Bond
As the Government of Mexico considered legislation to improve the country's management of solid waste, Coca-Cola FEMSA, in collaboration with bottling and plastics industry peers including PepsiCo bottler GEPP, supported the establishment of ECOCE (Ecología y Compromiso Empresarial, or Businesses Committed to Environmentalism), a non-profit dedicated to improving recycling rates in Mexico. Using price incentives to encourage greater PET bottle collection, the consequent increase in recycling rates and reliability of local rPET (recycled PET) feedstocks helped mobilize capital to develop local recycling infrastructure. Early on, this capital was sourced from the International Finance Corporation (IFC), a private sector-focused global development institution, and other commercial return seeking institutions. Subsequent capital came from recycled plastic stakeholders in Mexico — most recently through investment by Coca-Cola FEMSA funded by the tightly priced issuance of a green bond, for which Morgan Stanley served as joint bookrunner. The aggregated capital helped create domestic PET processing infrastructure, broadened he number of market participants engaged in tackling plastic waste, and increased the quantity of recycled material in plastic packaging in Mexico.
GPAP (2022), Unlocking the Plastics Circular Economy: Case Studies on Investment
Fortuna Cools
Founded in 2018, Fortuna Cools, a Philippine startup, works alongside small-scale agricultural communities and offers coolers and insulated packaging made from up-cycled, biodegradable coconut fibers to help fishermen preserve their catch without relying on fragile Styrofoam boxes. The coolers offer communities a more robust and lower cost cold storage solution. In 2021 the UN Development Program awarded Fortuna's Coconut Cooler the Ocean Innovation Prize for accelerating the shift from plastic foam to biodegradable alternatives. Fortuna Cools secured a seed investment round led by ADB Ventures (the impact investment arm of Asian Development Bank) and Katapult Ocean Fund.
Indorama Ventures Blue Loan
With strong demand from its global customer base and a drive to advance its own environmental, social, and corporate governance (ESG) credentials, Indorama Ventures Ltd. (IVL), the world's largest producer of PET bottles, committed to double its recycling capacity by investing $1.5 billion in processing facilities across five strategic emerging markets. To achieve this, IVL secured a blue loan financing package valued at $300 million from three development finance institutions (DFIs): the International Finance Corporation (IFC), Asian Development Bank (ADB), and Deutsche Investitions- und Entwicklungsgesellschaft (DEG). The new financing generated further investment in recycling infrastructure by IVL. This innovative financial instrument is the world's first independently verified, non-sovereign blue loan, and has fostered the development and acceptance of issuance guidelines for the nascent blue bond market.
GPAP (2022), Unlocking the Plastics Circular Economy: Case Studies on Investment
Landfill in Albania
KfW, a German development bank, lead the financing of a EUR27.5m funding package to Albania to finance a programme for sustainable solid waste management in the Vlora district. The programme focused on the construction of a new regional sanitary landfill for solid waste, sorting and composting facilities, equipment, and closure of existing dumpsites in the Vlora area.
Financing Experiences and Opportunities for SWM in Albania
Natura Sustainability Linked Bond
In 2021, Natura Cosméticos S.A. (Natura), a wholly owned subsidiary of Natura &Co, issued a sustainability linked bond (SLB). One of the objectives of the bond was increased use of recycled plastic in the company's packaging. A majority of Latin American SLBs to date have also included GHG reduction targets, alongside a recycled plastics mandate (as Natura did) that positions the circular economy as an instrument to attain climate objectives. Natura's bond garnered strong investor interest, with Morgan Stanley acting as joint bookrunner. Building incentives into Latin American SLBs for issuers to meet their ESG targets could underpin increased issuance in other emerging markets, where accountability and transparency are often lacking.
GPAP (2022), Unlocking the Plastics Circular Economy: Case Studies on Investment
Paboco Joint Venture
Paboco (The Paper Bottle Company) was founded in 2019 as a joint venture between ALPLA and pulp and paper manufacturer Billerud. Together with the Pioneer brands Carlsberg, L'Oréal, Coca-Cola Europe, and Absolut as well as its technology partners, Paboco is working intensely on realizing its long-term objective: the development and scaling of a fully bio-based, recyclable, fiber-based bottle made of renewable materials. This bottle could replace both single-use glass bottles and plastic bottles. After the successful test phase, series production of the next generation of recyclable paper bottles is scheduled to start at the end of 2024.
Denmark's Paboco to produce fully recyclable paper bottles at new facility in 2024
Plastic Energy
Plastic Energy is a chemical recycling solution providers which converts end-of-life plastic waste into feedstock for making virgin-quality recycled plastics. Plastic Energy has two chemical recycling plants in operation in Spain. Plastic Energy has agreements with chemical and oil and gas companies including SABIC, TotalEnergies and ExxonMobil to expand its recycling capabilities. Plastic Energy project portfolio includes plans to build large scale plant in Malaysia, Indonesia, as well as in Europe. In 2022, Plastic Energy raised EUR145m from financial investors and corporate funding to accelerate its growth and expand its portfolio of recycling plants.
Plastic Energy Completes €145 Million Fundraise
Project STOP Indonesia
Launched in 2017 by Borealis and Systemiq, Project STOP (STop Ocean Plastics) works hand in hand with city governments to create effective circular waste management systems in high need areas of Southeast Asia. The initiative supports cities with technical expertise to achieve zero leakage of waste, increase recycling, build economically sustainable programs, creating new jobs and reducing the harmful impact of mismanaged waste on public health, tourism, and fisheries. While the first city partnership was established in 2017 in the municipality of Muncar, East Java in February 2022. Project STOP Muncar was handed over to the local government and communit y. Now the programme expands to the Banyuwangi regency combines a regency level waste system model with a material aggregator into a circular waste and recycling solution that can transform waste economics. Project STOP also operates two additional city part ner ships, in Pasuruan Regency, East Java where the programme is now fully owned by local authorities and the community in February 2023, and Jembrana Regency, in Bali. Project STOP's corporate partners include the Nestlé, Borouge, the Alliance to End Plastic Waste, Siegwerk, Shwarz, and HP, with support from Trusts & Foundations, P4G and Accenture, including Academia, Pisces. Project STOP's success is in large part thanks to these collaborations as well as its close partnership with Norwegian government, USAID, local and national government offices in Indonesia, including the National Ministry for Environment and Forestry (KLHK) and the Coordinating Ministry for Maritime and Investment Affairs (CMMAI) and the Regency governments in the regions it works.
Recykal
The Indian government's Swaach Bharat (Clean India) mission helped to catalyze Recykal's solution to bring transparency and traceability to India's plastic waste supply chain via a digital platform. The waste management start-up secured $26 million in funding from domestic and international investors, including Morgan Stanley, in just three years. By encouraging the migration of plastic waste transactions to a digital marketplace, Recykal's model also promises greater standardization and reliability of associated data, bolstering the investment case for allocating capital to the sector.
GPAP (2022), Unlocking the Plastics Circular Economy: Case Studies on Investment
Solid Waste Management Project in Peru
In 2012, the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) signed ODA loan agreements with the government of Peru to provide loans of up to 8.77 billion yen for assistance for the Energy Renovation Infrastructure Assistance Program and up to 4.396 billion yen for assistance for the Solid Waste Management Project. The objective of the Solid Waste Management Project is to establish efficient and sustainable solid waste management system in the 23 prioritized cities by constructing solid waste infrastructures as well as developing and/or rehabilitating solid waste collection and recycling/ recovering systems thereby contributing to improve environmental quality and living standard of the people in the target regions in Peru. It also aims to contribute to the alleviation of climate change. Through this project, JICA will assist the first trial of the central government of Peru to undertake and supervise the nationwide program to construct an integral waste management system in many local cities, which will be a crucial step for the development of waste management system in Peru. Coordinating with the IDB, JICA will advance the project while providing appropriate assistance to MINAM, which will supervise the project. The possibility of technical cooperation, dispatching volunteers and other such steps are also being considered for enhancing the capacity of the local municipalities to operate, maintain and manage the facilities constructed and settled by this project, as is assistance for environmental-education to the residents. The funding for this project will be allocated to civil works for the construction of sanitary landfills, procurement of materials and equipment (including heavy machinery for sanitary landfills and vehicles for collection and transportation of waste) and consulting services.
Signing of Japanese ODA Loan Agreements with the Republic of Peru
Tridi Oasis
Tridi Oasis was founded in 2016 by two women entrepreneurs as a processor of post-consumer PET bottles into flakes. Beyond the founders' start-up funds, seed capital was provided by a local venture firm and a Java-based non-profit. By 2019, Tridi Oasis had expanded its capacity and needed additional capital. Circulate Capital's Ocean Fund, a blended finance vehicle offering early-stage venture debt and equity, extended its first loan to Tridi Oasis in early 2020. The loan benefited from a 50% credit guarantee provided by the U.S. International Development Finance Corporation (DFC), which partially de-risked the fund's investment while allowing the founders to maintain their existing equity. A second loan in early 2021 combined with technical assistance allowed Tridi to maintain operations through the Covid-19 pandemic and even increase productivity. Ultimately, in 2022 the company was able to attract an experienced strategic partner and pursue further expansion.
GPAP (2022), Unlocking the Plastics Circular Economy: Case Studies on Investment
Waste-to-Energy and Waste Treatment Project in Vietnam
In 2022, the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) signed a US$ 7 million loan agreement with Binh Duong Water Environment Joint Stock Company ("BIWASE") in Vietnam. This loan is co-financed by the Asian Development Bank (ADB). The US$ 6 million from ADB will be financed through the Leading Asia's Private Infrastructure Fund (LEAP), which is funded by JICA and administered by ADB. This project aims to contribute to the improvement of the urban environment and the circular economy in the region by financing the construction of a composting plant with a capacity of 840 tons per day and a waste-to-energy incineration facility to process 200 tons per day. BIWASE, the borrower of the project, established in 1975 and privatized in 2016, is a water-supply and waste-treatment company, and is the sole waste-treatment company that provides general waste treatment in Binh Duong Province.
Bueno Aires waste collection systems
In 2014, the municipality of Buenos Aires, Argentina, contracted the management of its waste management services to Proactiva Medio Ambiente, a Veolia subsidiary. The ten-year contract represents cumulative revenues of €500 million. Proactiva is responsible for collecting solid household waste and urban cleaning services in central Buenos Aires. To improve both service performance and health conditions, Proactiva implemented a waste containerization system throughout the service area.
IFCO acquisition by PE fund Triton
In 2019, IFCO SYSTEMS, a leading global provider of reusable packaging solutions for fresh foods, was acquired by to Triton, a private equity fund, and the Abu Dhabi Investment Authority (ADIA), for an enterprise value of US$ 2.51 billion. At the time IFCO generated revenues of more than US$1.1 billion.
IFCO announces acquisition by Triton for US$ 2.5 billion - IFCO Systems
Circolution receives seed funding from Amcor
In 2023, Amcor, a global leader in developing and producing packaging solutions, has announced a $250,000 investment into smart reusable food packaging start-up Circolution, the third winner of Amcor's Lift-Off initiative. Launched in April 2022, Amcor Lift-Off targets breakthrough, state-of-the-art technologies that will further advance Amcor's goal to make the future of packaging more sustainable. Circolution is the third company to secure funding through Amcor's Lift-Off initiative, which offers packaging start-ups up to $250,000 investment (convertible loan) to help scale their innovations, as well as access to Amcor's research and development resources.
Notpla raises £10M to develop seaweed-based packaging
In 2021, Notpla, a London-based sustainable packaging startup, has recently secured £10 million in a Series A funding round. This round was led by Bangkok-based Horizons Ventures, with additional contributions from Astanor Ventures, Lupa Systems, and Torch Capital. Established in 2014 by Rodrigo Garcia Gonzalez and Pierre-Yves Paslier, Notpla aims to combat plastic pollution by creating packaging solutions from seaweed and plants. Their innovative approach aligns with the EU Single-Use Plastic Directive, offering products that biodegrade within 4-6 weeks without the need for industrial composting. Notably, Notpla has developed "Ooho", an edible and fully biodegradable packaging made of seaweed, which has replaced over 500,000 single-use plastics at major events. They have also introduced a seaweed-coated cardboard for food packaging, in collaboration with Just Eat Takeaway.com. The recent funding will boost manufacturing and support the development of new products like transparent flexible films and seaweed paper. Notpla's unique, sustainable solutions are gaining traction, and they plan to expand into the cosmetics and fashion industries, underscoring their commitment to a future free of single-use plastics.
Indonesia's Waste4Change raises $5m in series A funding
Waste4Change, an Indonesia-based waste management startup, recently secured a $5 million Series A funding, co-led by AC Ventures and PT Barito Mitra Investama, with notable contributions from Basra Corporation, Paloma Capital, and others. Since its inception in November 2014, the company has committed to addressing Indonesia's waste management challenges, focusing on reducing landfill waste and enhancing recycling efforts. This fresh infusion of capital is earmarked for expanding Waste4Change's waste management capacity to 100 tons per day within the next 18 months, aiming for a significant increase to 2,000 tons per day over the next five years. Integral to this expansion is the integration of digital technologies for enhanced waste management processes and the automation of material recovery facilities. Furthermore, the company plans to fortify partnerships within the country's informal waste sector. Waste4Change operates across 21 Indonesian cities, managing more than 8,000 tons of waste annually and demonstrating a robust growth trajectory, with a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 55.1% since 2017. Under the leadership of founder and CEO Mohamad Bijaksana Junerosano, Waste4Change is not only scaling its operations but also aligning with the Indonesian government's environmental objectives, reinforcing its commitment to sustainable waste management solutions.
Indonesia's Waste4Change grabs $5M Series A co-led by AC Ventures - TNGlobal (technode.global)
Coliba Africa
Coliba Africa is a Cote-d'Ivoire-based recycling and waste management start-up. The company received financing for a 28-month project integrating informal waste collectors into Coliba's business model and training them to build better businesses. Coliba received a grant from USAID West Africa Trade & Investment Hub totalling $850,000, to implement its training and capacity building project. The Trade Hub grant with a loan from the Alliance to End Plastic Waste, and other stakeholders will fund a project to train 6,000 informal waste collectors, set up modern waste collection and recycling facilities with a capacity of 14,000 tons per year. The Alliance also provided the technical expertise needed to help the project develop a holistic waste management ecosystem.
World Bank's Plastic Policy Simulator (PPS)
Plastic Policy Simulator (2022)
GPAP National Analysis and Modeling (NAM) Tool
GPAP's National Analysis and Modeling (NAM) Tool allows countries to establish a science-based roadmap to accelerate their transition to a circular, low carbon emissions plastics system. It has been implemented in 12 countries to date.
Global Plastic Action Partnership NAM Tool
The Circulate Initiative’s Plastics Circularity Investment Tracker
The Circulate Initiative's Plastics Circularity Investment Tracker provides insights into private investments in plastics circularity globally.
Plastics Circularity Investment Tracker, The Circulate Initiative
Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee on Plastic Pollution (INC)
Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee on Plastic Pollution (INC)
UNEP Zero draft text of the international legally binding instrument on plastic pollution
Unlocking the Plastics Circular Economy: Case Studies on Investment
Unlocking the Plastics Circular Economy: Case Studies on Investment, GPAP (2022)
Redirecting financial flows to end plastic pollution
Redirecting financial flows to end plastic pollution, UNEP-FI (2023)
Breaking the Plastic Wave
Breaking the Plastic Wave, Systemiq
Mobilizing Blended Finance for Circular Waste Collection and Sortation
Mobilizing Blended Finance for Circular Waste Collection and Sortation, Systemiq (2023)